Plastic valves are essential components in various industries, facilitating the control and management of fluid flow. As an expert in the field, Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned materials scientist and engineer, emphasizes the significance of these valves, stating, "Plastic valves have revolutionized fluid handling by combining lightweight design with exceptional corrosion resistance." This statement underlines the transformative impact of plastic valves in applications ranging from water treatment to chemical processing.
In different industrial settings, the unique properties of plastic valves, such as durability and versatility, make them ideal for challenging environments where traditional materials may fail. Their ability to resist chemical reactions and withstand pressure makes them indispensable in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and petrochemicals. As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and cost-effectiveness, the adoption of plastic valves continues to grow, demonstrating their fundamental role in modern engineering solutions.
As we delve deeper into the functioning and applications of plastic valves, it becomes evident that their innovative designs and material properties are not only enhancing operational efficiency but also contributing to environmental initiatives. Understanding how these valves work and their versatility across various sectors reveals the vital role they play in today’s interconnected industrial landscape.

Plastic valves are components made from various types of plastics, designed to control the flow of fluids in a multitude of applications. Their composition typically includes materials such as PVC, CPVC, and polypropylene, known for their resistance to corrosion, low weight, and cost-effectiveness. These properties make them an attractive alternative to traditional metal valves in industries like water treatment, chemical processing, and food and beverage. The versatility of plastic allows these valves to be manufactured in various sizes and designs to suit specific requirements, providing reliable functionality across different sectors.
The understanding of plastic valves goes beyond their material makeup; it also involves understanding how their design influences performance. For instance, the smooth surface of a plastic valve minimizes turbulence, which is crucial for maintaining fluid integrity in sensitive processes. Moreover, innovations in plastic technology have led to developments in the composition of these valves that enhance their durability and operational efficiency under diverse environmental conditions, similar to how advancements in understanding bacterial biofilms have improved treatment strategies in the healthcare sector. As industries continue to evolve, the role of plastic valves in optimizing performance and ensuring safety will likely expand further.
This chart illustrates the distribution of plastic valve applications in various industries. The data highlights the significant role of plastic valves in sectors such as Chemical Processing, Water Treatment, Food and Beverage, and Pharmaceuticals.
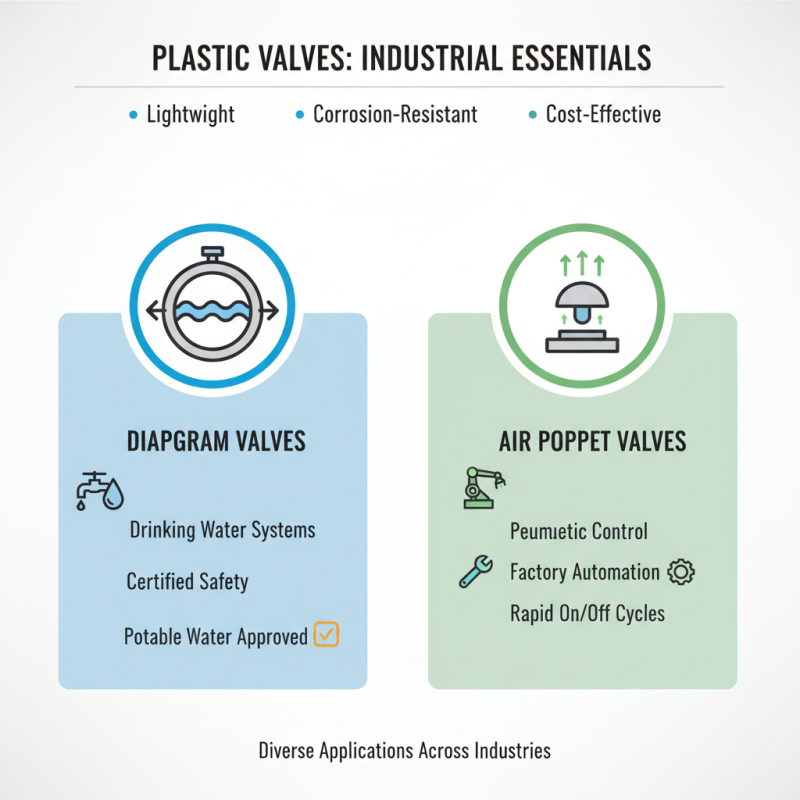
Plastic valves play a crucial role across various industries, primarily due to their lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective nature. Among the different types of plastic valves used, diaphragm valves and air poppet valves stand out for their specific applications. Diaphragm valves, for instance, are often used in drinking water supply systems, where certified safety is paramount. This is evident as many manufacturers produce plastic diaphragm valves that meet stringent regulatory standards for potable water use.
In terms of market dynamics, the global industrial valve market is projected to expand significantly, with estimates indicating it will reach a valuation of $121.67 billion by 2024. This growth is fueled by increased investments in water supply and distribution systems, where PVC pipes and fittings are extensively utilized. The versatility of plastic valves, like those in the expanded air poppet valve series, is particularly noteworthy as they support mold ejection processes in plastic injection molding, indicating their importance in manufacturing sectors as well. Such advancements in valve technology reflect ongoing innovations aimed at improving efficiency and safety across various applications.
Plastic valves are essential components in various industries, functioning based on intricate mechanisms that ensure efficient fluid control. These valves operate using a simple yet effective design, typically comprising a body, a seat, and a closure element. The closure element can be a disk, ball, or other shapes that move to open or close the flow pathway, which is usually actuated manually or automatically. For instance, in the chemical industry, plastic valves are pivotal due to their corrosion resistance and lightweight nature, allowing for safe handling of aggressive fluids.
The mechanisms of operation in plastic valves can be likened to biological systems, such as the precibarial valve in hemipteran insects. This tiny structure plays a crucial role in controlling fluid flow necessary for probing behaviors, emphasizing the importance of precise regulation in both biological and mechanical contexts. Similarly, advancements in engineering have enhanced valve designs, evident in applications like the highly resilient high-entropy alloy coatings for fracturing pump valves. These innovations improve performance and longevity, showcasing how understanding operational mechanisms can lead to significant advancements in valve technology across numerous sectors.
Plastic valves have become increasingly integral in various industrial applications, primarily due to their lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. In sectors such as water supply and distribution, plastic valves are preferred for handling liquids and gases safely, making them ideal for both residential and industrial infrastructures. The Europe plastic valves market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% by 2032, highlighting the ongoing shift toward plastic materials over traditional options like steel.
Tips: When choosing plastic valves for industrial uses, consider the specific material properties, such as UPVC and CPVC, which are known for their durability and resistance to various chemicals. Assess the compatibility of these materials with your application to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Furthermore, advancements in design and manufacturing processes continue to enhance the functionality of plastic valves. Leading manufacturers are focusing on high-impact plastic valve guards to improve safety and reliability in operations. As the global plastic valves market is anticipated to hit USD 4.2 billion by 2032, industries are encouraged to explore innovative solutions that meet evolving safety standards while optimizing cost and efficiency.
Tips: Regular maintenance of plastic valves is essential to prolong their lifespan and ensure operational efficiency. Conduct periodic inspections and replace any components that show signs of wear or damage to maintain system integrity.
Plastic valves have gained popularity across various industries due to their inherent advantages. One significant benefit is their lightweight nature, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. Additionally, plastic valves are resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical processing and wastewater treatment. Their lower thermal conductivity also makes them well-suited for applications involving temperature fluctuations, ensuring durability over time.
However, there are limitations to consider when using plastic valves. They typically have a lower pressure and temperature tolerance compared to their metal counterparts, which may restrict their use in high-stress applications. Furthermore, while they are resistant to many chemicals, certain solvents and high-temperature substances can degrade plastic materials. This necessitates careful material selection based on the specific application requirements. Ultimately, understanding these advantages and limitations helps industries make informed choices when integrating plastic valves into their systems.
| Industry | Advantages of Plastic Valves | Limitations of Plastic Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Corrosion resistance, lightweight, and low-cost materials | Limited temperature and pressure ratings |
| Water Treatment | Chemical resistance, easy installation, and maintenance | Potential for UV degradation |
| Food and Beverage | Non-reactive materials, FDA-approved options available | Possible leaching of chemicals under certain conditions |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilizable and corrosion-resistant | Limited mechanical strength compared to metals |
| HVAC Systems | Lightweight and ease of installation | Higher thermal expansion rates than metal |





Cepex is the brand for the fluid handling market belonging to the Fluidra group. One of the leading european manufacturer of valves and fittings in thermoplastic materials.
Dedicated to the swimming pool, irrigation and industrial markets, we distribute our products worldwide with the Fluidra commercial network and presence in 46 countries with 136 sales branches.
