Ball valves are an essential component in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications, known for their reliability and durability in fluid control systems. These valves operate using a spherical disc, or "ball," which serves as the closing mechanism. By simply rotating the ball within the valve body, the flow path can be opened or closed, allowing for efficient management of liquids and gases. This unique mechanism makes ball valves highly effective in situations where a quick shut-off is necessary, emphasizing their significance in various sectors, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
The versatility of ball valves extends beyond their basic function; they are designed to endure high-pressure and high-temperature environments, making them suitable for challenging conditions. Their ability to maintain a tight seal ensures minimal leakage and enhances safety, which is critical in applications where hazardous materials are handled. Moreover, ball valves are favored for their ease of operation and low maintenance requirements, contributing to operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in many systems. With these attributes, ball valves have become a preferred choice in modern fluid management solutions, playing a vital role in enhancing the performance of diverse industrial processes.
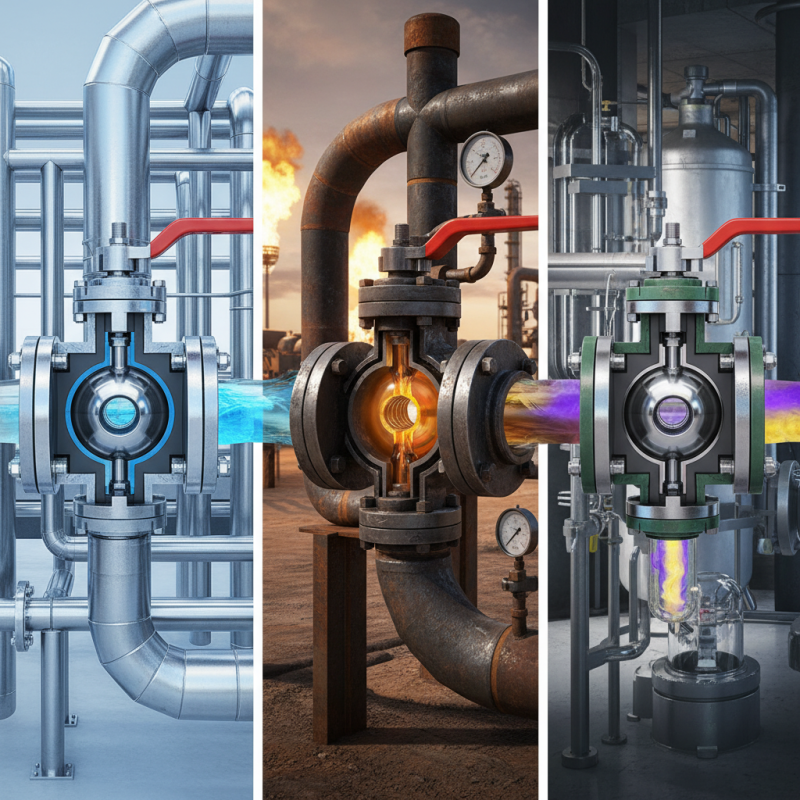

A ball valve is a type of quarter-turn valve that uses a spherical disc, or ball, to control the flow of fluid through a pipe. The ball has a hole in the center, allowing fluid to pass through when aligned with the flow. When the valve is closed, the ball is rotated 90 degrees, blocking the flow completely. This simple yet effective mechanism makes ball valves particularly desirable for applications requiring rapid shut-off and reliable sealing.
In various industries, ball valves are utilized due to their versatility and efficiency. In water supply systems, for instance, they provide a straightforward means of controlling water flow, allowing for quick maintenance and repairs. In oil and gas applications, their robust construction ensures they can handle high-pressure environments while minimizing leaks. Furthermore, ball valves are also found in chemical processing, where they regulate corrosive fluids while maintaining safety and operational integrity. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures makes them a go-to choice across numerous sectors, highlighting the importance of ball valves in modern infrastructure.
| Application | Material Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Stainless Steel | -50 to 200 | 1500 | Flow control in pipelines |
| Water Supply | PVC | 0 to 60 | 100 | Residential plumbing |
| Chemical Processing | Brass | -20 to 120 | 300 | Control of corrosive substances |
| HVAC Systems | Aluminum | -10 to 70 | 150 | Temperature control in buildings |
| Food and Beverage | 316 Stainless Steel | 0 to 100 | 200 | Ingredient transfer |
Ball valves are essential components in various piping systems, distinguished by their unique structure and design features. At the core of a ball valve is a hollow, perforated sphere – or ball – that serves as the closure element. This ball rotates within the valve body to either allow or restrict flow. The simplicity of this design facilitates a quick on-off mechanism, making ball valves highly efficient for controlling flow in a multitude of applications, from water supply systems to industrial processes.
The design features of ball valves also contribute to their versatility. Typically constructed from durable materials like stainless steel or plastic, they are built to withstand high pressure and temperature variations. The seats that encase the ball can be made from different materials, depending on the specific application requirements, which enhances their sealing capabilities and longevity. Additionally, ball valves can be operated manually or automatically, allowing for adaptations in various environments, from residential plumbing to complex industrial operations. Their compact design also allows for integration in confined spaces, making them ideal for diverse operational needs.
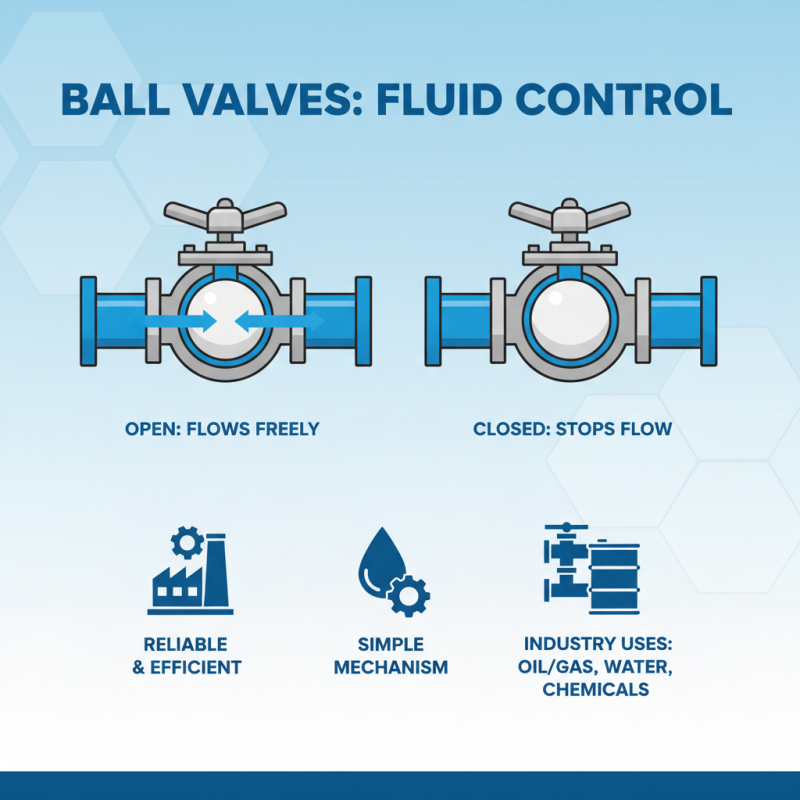
Ball valves are essential components in fluid control systems, known for their reliability and efficiency in regulating flow. These valves operate using a spherical disc, or "ball," that has a hole through its center. When the valve is open, the hole aligns with the flow direction, allowing fluids to pass through unobstructed. Conversely, turning the valve 90 degrees closes the hole, effectively stopping the flow. This simple yet effective mechanism makes ball valves a preferred choice in various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global ball valve market is projected to reach USD 16.14 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for reliable fluid control solutions across multiple sectors. Ball valves are particularly favored for their ability to maintain tight seals, which reduces the risk of leaks in high-pressure systems. Additionally, their quick on-off capabilities make them highly efficient for applications that require rapid flow control, such as in emergency shut-off systems or in processes where the flow needs to be adjusted swiftly.
In fluid control systems, ball valves also contribute to energy efficiency. Their design minimizes pressure drop across the valve, thereby reducing energy consumption in pumping applications. Furthermore, the widespread adoption of advanced materials for embankments in ball valve manufacturing enables them to withstand corrosive environments, enhancing their longevity and performance. This makes them suitable for not only conventional applications but also for more demanding scenarios, such as in the petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Ball valves are widely utilized across various industries due to their robust design and reliability in controlling the flow of liquids and gases. One common application is in the oil and gas industry, where ball valves are essential for regulating the flow and pressure of hydrocarbons. They provide a quick shut-off option, which is crucial in preventing leaks and ensuring safety in operations. Moreover, in the water treatment sector, ball valves facilitate the management of water flow, allowing for efficient system operations.
In food processing, these valves play a significant role in maintaining hygiene and controlling the flow of ingredients. Their smooth interior surfaces enable easy cleaning and maintenance, which is critical in preventing contamination. Chemical manufacturing also relies on ball valves for their ability to handle corrosive substances. The design minimizes leakage and withstands high pressures, making them a preferred choice for handling various chemicals safely.
Tip: When selecting a ball valve for a specific application, consider the temperature and pressure requirements, as well as the type of fluid being handled. Proper valve sizing is essential to ensure optimal performance and avoid unnecessary wear or failure in the system.
Additionally, ball valves are increasingly finding applications in renewable energy systems, such as solar and geothermal installations, thanks to their efficiency and reliability. Their simple quarter-turn operation makes them user-friendly, allowing for quick adjustments as needed.
Tip: Regular maintenance checks on ball valves can significantly extend their lifespan. Look for signs of wear or corrosion and replace any affected components promptly to ensure consistent performance.
Ball valves are widely recognized for their pivotal role in various industrial applications due to their unique design and operational efficiency. One of the main advantages of using ball valves is their ability to provide a tight seal, which effectively prevents leakage. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global ball valve market size was valued at approximately $9.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $12.4 billion by 2028, showcasing their increasing prevalence in sectors such as oil and gas, water and wastewater management, and chemical processing.
However, while ball valves offer numerous benefits, there are also disadvantages to consider. For instance, their operation requires more space compared to other valve types due to the full rotation of the ball to open or close the valve. Additionally, in throttling applications, ball valves can lead to high wear rates, as the fluid can cause erosion on the ball and seat surfaces. A technical analysis from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) highlights that incorrect installation and maintenance can further exacerbate these issues, leading to decreased performance and increased costs. Despite these drawbacks, when appropriately applied, ball valves remain a strong choice for many applications due to their durability and reliability.






Cepex is the brand for the fluid handling market belonging to the Fluidra group. One of the leading european manufacturer of valves and fittings in thermoplastic materials.
Dedicated to the swimming pool, irrigation and industrial markets, we distribute our products worldwide with the Fluidra commercial network and presence in 46 countries with 136 sales branches.
